Trademark Infringement in India
Is anybody attempting to pass off their product as yours? If that's the case, you need to take steps to stop the trademark infringement.
Today's market is hampered with brand infringement. Sadly, many people prefer the shortcut of dishonesty, trying to pass off their brand as their own, to the benefits of hard labor. Because of this, many companies are failing or simply disappearing into oblivion.
If you're not careful, trademark infringement involving your company's name or other brands might hurt your business, too. That's why it's important for you to investigate any trademark infringement in India. And we can assist you in doing just that.
What is trademark infringement in India?
It's important that we all have a common understanding of trademark infringement before we can effectively work together to stop it. Infringing on someone else's trademark is using their logo or name without their consent.
A trademark infringement occurs when one party's rights to use another's trademark are violated or when one party uses another's trademark without authorization.
The term "Trademark Infringement" needs a legal meaning, therefore let's look at one.
Infringing on a trademark means doing something that the trademark owner forbids without their permission or that of their licensees. When a third party uses a trademark that is identical to, or confusingly similar to, a trademark owned by another party regarding goods or services that are identical to, or similar to, the goods or services covered by the registration, an infringement may have occurred.
Trademark infringement is being criminalized.
Trademark owners can sue in civil court when their marks are stolen or otherwise violated. Selling fake goods or services is against the law in the United States thanks to the Trademark Counterfeiting Act of 1984.
A trademark that has not been registered cannot be "infringed" as such, and the owner of the trademark cannot bring infringement procedures, in many countries (but not in nations like the United States, which recognizes common law trademark rights). Alternatively, the owner may pursue legal action for passing off or misrepresentation under common law or under statutes forbidding unfair commercial practices. The unauthorized use of a company's trademark or logo is a civil wrong that can be pursued in some jurisdictions.
Ignoring even the most frequent form of trademark infringement would be a mistake, so why exactly is trademark infringement such a major deal? The financial burden that a business name trademark infringement can put on your enterprise might make it hard for you to cope with the losses.
Damage resulting from trademark infringement
Owning a trademarked brand name establishes your exclusive use of that name in the marketplace. In addition, having a well-known brand name ensures that consumers will purchase your wares. If someone were to take your company's name, you can probably predict the harm they would do to your bottom line:
Brand loyalty is eroding
Your clients have faith in your company because of your brand. The reputation of your company could suffer if someone else uses your trademark to market a low-quality knockoff. The subsequent loss of confidence and loyalty from customers can be devastating.
Customers may decide to avoid your company.
If you are accused of trademark infringement in India and don't hurry to submit a cease order, you risk having your customers swayed by your competitors into shunning your product. As a general rule, consumers are loath to put their faith in a company. Consequently, trademark infringement is the first thing that will turn off your customers.
Confused customers would fail to reach out to you: There is a 90% chance that an unhappy customer will not get in touch with you unless the problem is extremely bothersome. And because brand thieves count on confusing the customer, if something goes wrong, you won't get any calls from upset customers; instead, your prospects will simply ignore you.
You can lose your business: Consider what happens if your client completely disregards you. When your consumers run away, there is no business to be had. As a result, your business partners and creditors will lose faith in you and you will struggle to maintain your brand's visibility in India and other markets.
Therefore, in whatever instance that comes your way, preventing trademark infringement, no matter how minor, should be your primary priority.
In India, what are the many categories of trademark infringement?
The Intellectual Property Authority has classified trademark infringement into two categories:
Direct Infringement
Indirect Infringement
Direct Trademark Infringement
Section 29 of the Trademark Act defines direct trademark infringement. The following are the conditions of trademark infringement in this case, according to this section:
Unauthorized Person Using a Trademark
Only when an unauthorized person uses the registered trademark is the trademark considered infringed. In other words, someone who is not authorized to use the trademark. In India, if an authorized user is utilizing the brand name, there is no case of trademark infringement.
Identical or Deceptively similar Trademark
In this case, the trademark in use may be deceptively similar or identical to an existing trademark in India. The term "deceptive" refers to the fact that a typical customer may become confused between similar brands and mistake them for the same. In a legal setting, the term "may" is sufficient to demonstrate that there is a chance of infringement if the brand names are too close. Even a remote possibility of misrecognition might be detrimental to the brand. As a result, identical or deceptively similar trademarks come under the category of direct infringement.
Valid on a Registered Trademark
All of the legal remedies for trademark infringement listed under the Direct Infringement of Trademark section are only applicable to registered trademarks. As a result, these restrictions will not apply in the case of an unregistered trademark.
Goods or Services class
The unauthorized user violates trademark regulations when he or she uses the trademark to sell goods and services in the class for which the trademark has been registered.
These are all direct incidents of violations. They are virtually always evident and simple to pursue. However, there is another type of trademark infringement lawsuit in which the crime is not as obvious. In India, such cases are referred regarded as indirect trademark infringement cases.
Indirect Infringement
Indirect trademark infringement is defined in the Trademark Act 1999 as a type of infringement for which no provisions exist. To deal with issues of indirect infringement, trademark registration courts apply the universal concept. According to these principles, not only the offender, but also the person or group of people who causes trademark infringement is held liable.
In India, what are the many categories of indirect trademark infringement?
Some of the many facets of indirect trademark infringement in India are as follows:
Vicarious Liability
According to Section 114 of the Trademark Act, any corporation committing trademark infringement is subject to vicarious liability. It means that a corporation as a whole will have to accept responsibility if any of its employees commits trademark infringement in India. While it would be considered indirect trademark infringement, the entire organization would be subject to trademark infringement fines in India.
The following are the key aspects of Vicarious liability under trademark infringement rules:
The members of the company are aware of the infringement.
Members of the company participated in the act of infringement.
The major infringer was convinced or induced to commit the act by the company.
Note: There is no way to get around the rules. In many cases, people who break trademarks say that they did so in good faith. But in the eyes of the Indian government, everyone who helped commit a crime was almost as responsible, no matter how much "good faith" they had when they did it.
Contributory Infringement
Contributory Infringement is when someone has helped infringe on a trademark, either directly or indirectly. Contributory Infringement is made up of the following parts:
When the person knew about the violation,
When the person did something that broke the law,
When the company convinced or pushed the main person who broke the law to do it.
How should Trademark Infringement in India be handled?
If you don't want your brand to be taken by someone else, you must make sure that anyone who steals your brand faces the following consequences:
Talk to your infringer
Brand infringement is not always done illegally. People have a hard time distinguishing between being inspired by someone else and actually replicating what they did. That's why it's important to have a conversation with the people who are violating your trademark before sending a cease letter. You can proceed with trademark infringement proceedings in India if the offending party agrees to immediately cease all infringing activity and pays all damages awarded. To clarify, we do not recommend initiating contact with a trademark infringement warning letter.
Filing a complaint to the Trademark Authorities
An method based on peaceful negotiation with a trademark offender has some merit, but is rarely successful. After that, you can go ahead and file a formal trademark infringement case with the appropriate authorities. Because of this, you should be awarded a substantial sum of money if your brand was infringed upon in India.
Cease from Trademark Infringement in India
Choose the cease letter for trademark infringement if your brand is precious and any infringement could do irreversible damage to its reputation. Get in touch with a lawyer, have him draw out a template for a cease letter, and use that to your advantage in getting the infringement to stop using your trademark.
Use Legal Means (both Civil and Criminal)
You can use various civil and criminal remedies of Infringement if you wish to adopt a straightforward, no-nonsense approach to individuals who are attempting to steal your brand name. Compensation for losses incurred as a result of trademark infringement's illegal activity in India may be possible.
File for a Preliminary Injunction
Obtaining a preliminary injunction is the most effective strategy for dealing with trademark infringement. When you have reasonable grounds to suspect that someone is infringing on your trademark rights, you can petition for a trademark infringement lawsuit. For a short while, it will prevent the alleged trademark infringement. Not ideal, but it will assist you take the case to court till trademark infringement is criminalized in India. Keep in mind, nevertheless, that this is the proper response to accusations of trademark infringement. It could backfire if you end up losing the lawsuit.
A Permanent Injunction Petition
The most prevalent strategy for dealing with trademark infringement matters today is to issue a permanent injunction. You have a good possibility of success, and it may be enough to stop your infringer in his or her tracks. There is a price, though. The typical expense of a litigation for trademark infringement might skyrocket depending on how well-known the trademark is.
Trademark Infringement and the Various Remedy Options in India
The many legal options available to victims of trademark infringement in India are as follows:
Consequential damages for trademark infringement cases
Disciplinary Actions for Trademark Violation
Administrative Remedies for Trademark Infringement
What are Remedies?
For both unregistered and registered trademark infringement, remedies are available as forms of redress. When a trademark is violated, a lawsuit can be filed with the use of these legal resources.
Trademark Infringement and Civil Remedy
Indian Trademark Infringement Notice Formats
In the event of a trademark infringement, the Trademark Act of 1999 provides the following civil remedies:
Injunction
Permanent or temporary, injunctions are the legally binding orders of a judge.
Permanent Injunction refers to the order that the one against whom a notice of trademark infringement has been filed must follow forever, unless otherwise stated.
Temporary Injunction refers to the temporary order that the alleged infringer must adhere to.
Infringement Damages
The offended party may request damages for trademark infringement on legal grounds. It is relevant, however, only when the infringer has discontinued activities and it has been established that the aggrieved party has sustained a loss. It is considered for determining trademark infringement damages in India.
Civil remedies govern the handling of profit accounts and the elimination of infringing products.
Criminal Penalty for Trademark Infringement
In terms of criminal remedies, the Trademarks Act of 1999 outlines the penalties for trademark infringement in India.
Imprisonment
In India, the most basic criminal action for trademark infringement is imprisonment for six months, which can be extended to three years based on the severity of the conduct.
Financial penalties
Another portion of the criminal remedies against trademark registrations stipulates that anyone who violates another's trademark rights must pay a penalty of 50,000 rupees.
Taking Possession of the Property
The civil and criminal consequences for trademark infringement can also result in the forfeiture of the infringer's property in order to pay for the damages caused by the trademark infringement.
Trademark Infringement Administrative Remedies
The following points are included in the palette of administrative remedies:
Opposition to a trademark
During the trademark registration procedure, trademark authorities have the authority to investigate the to-be-registered trademark.
Correction to a Trademark
To avoid brand confusion, the applicant may make changes to the registered trademark.
Examining the trade activity
Before taking action, the authorities might investigate the activity - products or services - on which the infringing trademark is used.
Defendants Against Infringement
Before pursuing legal action for trademark infringement, the applicant must first determine whether there is an infringement case. Because intellectual property regulations might be difficult to understand, baseless threats of trademark violation are becoming increasingly widespread. As a result, it is necessary to understand which instances should not be regarded as infringement in India:
The trademark in issue has not been used in anyway that could harm its reputation or distinctive character.
When a registered trademark is used to communicate the quality, purpose, geographical origin, time of manufacture, or other attributes of a product or service.
When the trademarks are identical to one another
When the trademark is applied to parts and accessories,
When the brand is used in accordance with the trademark act's regulations
The preceding points can be utilized to provide arguments in trademark infringement proceedings in India.
Trademark Infringement Eligibility Requirements
All the facts that can support your case against Trademark Infringement must be formulated before you can go up against it. Here are the bare minimums that must be met to establish trademark infringement:
In order to avoid confusion, the proposed trademark should be either an exact match or a confusingly similar version of an existing trademark.
This trademark was designed to be harmful to your reputation.
Because no direct provisions exist for indirect cases of trademark infringement, infringement should be obvious.
The legal costs associated with a criminal trademark infringement claim should be within your means.
Damages for trademark infringement require supporting evidence, which you must provide to the court.
Trademark Infringement Documents
This section describes a checklist of things you'll need to prove your case against trademark infringement. Both physical and electronic copies of these trademark infringement requirements must be maintained by the applicant.
Certificate of Trademark Registration
Arguments for trademark infringement
Warning of trademark infringement lawsuit
Everything you need to win your trademark infringement lawsuit
File explaining why you think there was trademark infringement
You need proof of past usage of a trademark in order to file a trademark infringement lawsuit.
All of the above must be signed and overseen by a competent trademark attorney before they can be filed.
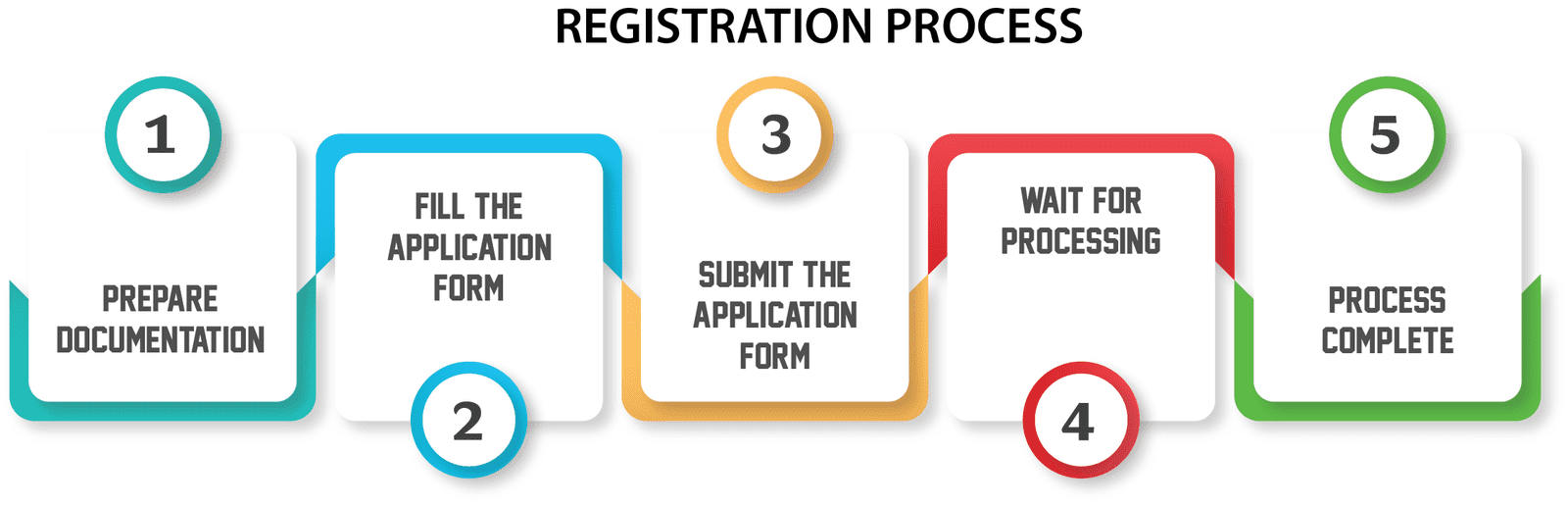
Trademark Infringement Process
The procedure for Trademark Infringement is as follows:
You have two options for dealing with your trademark infringement case in India.
Civil Law Procedure for Trademark Infringement
If you wish to take a less harsh approach to the trademark infringement lawsuit, you must adhere to the following guidelines:
A trademark infringement case can be filed in District Court under Section 134 of the Trademark Act of 1999.
Following that, the court will issue an injunction order. This would eventually entail the payment of damages to profit accounts and the elimination of infringing labels.
Criminal legal procedure for trademark infringement
Take a more vengeful stance in dealing with your infringer. To deal with the criminal charge of trademark infringement in India, you can take the following strategy.
File a police report against the infringer. You can make a complaint with the magistrate if the police refuse to file a FIT.
The trademark inquiry begins after the FIR is filed or the magistrate's ruling is issued. If your trademark infringement grounds are true, the products will be seized.
Criminal remedies for trademark infringement allow the applicant to sue unknown individuals.
We'll help you submit a trademark infringement claim.
Certpedia offers comprehensive services to address trademark infringement. Among the many things we offer are:
Data gathering and initial action
Formulating the application draft
Conducting a thorough reading of the document and revising it as needed
Legal Representation for Trademark Violation Claims
Certpedia is an industry-leading trademark infringement consulting organization. If you'd want us to represent you in a trademark infringement lawsuit, please get in touch with us as soon as possible.